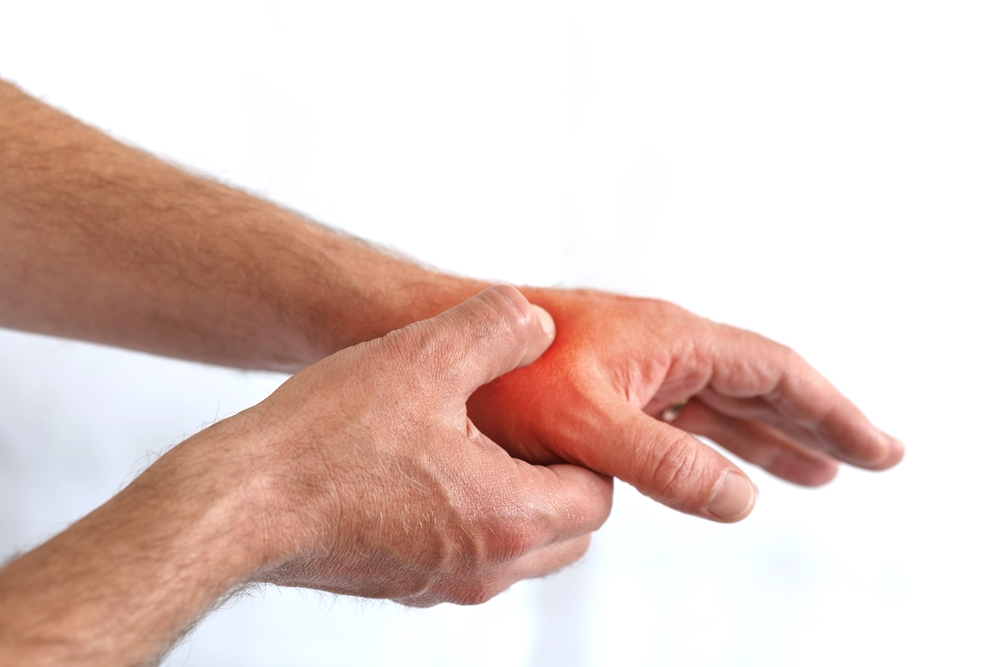
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, is compressed. This can lead to symptoms like numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain in the hand and wrist. If left untreated or if certain activities are continued, CTS can worsen over time. Let’s explore the main reasons why carpal tunnel syndrome may be worsening and the steps you can take to manage or even reverse its progression.
Repetitive Hand and Wrist Movements
One of the main culprits in the progression of carpal tunnel syndrome is repetitive movement. Actions such as typing, using a mouse, gripping tools, and playing musical instruments can lead to prolonged pressure on the median nerve, causing further inflammation and compression. If you frequently engage in these activities without adequate breaks or proper wrist positioning, the median nerve becomes more stressed, worsening CTS symptoms over time.
Practicing good ergonomics and taking regular breaks from repetitive tasks can make a significant difference. Wrist braces and supports may also help reduce strain on the carpal tunnel during certain activities.
Incorrect Wrist Posture
Poor wrist posture is a leading factor that can exacerbate carpal tunnel syndrome. If you keep your wrist bent for prolonged periods—whether while working, sleeping, or engaging in hobbies—it puts undue pressure on the median nerve. Bending the wrist too far forward or backward can irritate the nerve, inflaming the carpal tunnel area and worsening symptoms.
Keep your wrist in a neutral position as much as possible. When typing or using a mouse, avoid excessive bending by adjusting your workstation. Wrist splints, especially at night, can help keep your wrist in a neutral position and reduce symptoms.
Health Conditions That Increase Inflammation
Some medical conditions, like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and hypothyroidism, can contribute to inflammation in the body, making it more likely for carpal tunnel syndrome to worsen. Diabetes, for example, can cause nerve damage, which can make carpal tunnel syndrome more severe. Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can add to the swelling within the carpal tunnel, compressing the median nerve further.
Managing underlying health conditions can help alleviate CTS symptoms. Regularly consulting with a healthcare provider, maintaining blood sugar levels, and controlling inflammation are critical for preventing the worsening of CTS symptoms.
Inadequate Rest and Overuse
Overuse of the hands and wrists without adequate rest periods can make CTS worse. Constant strain on the wrist without recovery time doesn’t allow for inflammation to subside, leading to a cycle of irritation and compression in the carpal tunnel. This is particularly true for people whose work or daily activities involve long hours of typing, driving, or other repetitive wrist movements.
Take frequent breaks, especially if you’re engaged in tasks that involve repetitive motions. Rest and alternating activities can prevent continuous strain on the wrist, giving the median nerve a chance to recover.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Studies have shown that excess body weight is a risk factor for carpal tunnel syndrome. Weight gain, particularly in the wrist and forearm areas, can increase pressure within the carpal tunnel, exacerbating symptoms. Additionally, obesity can lead to systemic inflammation, which may aggravate CTS symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight can relieve pressure on the carpal tunnel and reduce inflammation. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and mindful weight management can not only help prevent CTS progression but also improve overall health.
Aging and Natural Degeneration
As we age, natural wear and tear in the joints and tissues can cause the carpal tunnel to narrow. This age-related degeneration can make the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome more pronounced, especially in people with arthritis or those who have had previous wrist injuries.
While aging is an inevitable factor, focusing on good ergonomics, regular stretching, and gentle wrist-strengthening exercises can help keep symptoms in check. Consult a doctor or physical therapist for exercises suited to your needs.
Ignoring Early Symptoms
One of the biggest reasons why carpal tunnel syndrome worsens over time is the lack of prompt treatment. Many people ignore early warning signs, like numbness or tingling, assuming they will go away. However, without addressing the underlying causes, the condition often worsens, making it harder to manage and treat.
Early intervention is key to preventing CTS from worsening. If you notice symptoms, consult a healthcare provider as soon as possible. Conservative treatments like wrist splinting, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy are often effective when implemented early.
Treatment Options for Worsening Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
If carpal tunnel syndrome continues to worsen despite taking preventive measures, you may need to explore medical treatments. Here are a few options to consider:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises that target wrist flexibility, strength, and nerve gliding can help alleviate pressure on the median nerve. A physical therapist can provide tailored exercises to relieve symptoms.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, including NSAIDs, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms temporarily. In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used for short-term relief.
- Surgical Options: If conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Carpal tunnel release surgery involves cutting the ligament pressing on the median nerve, providing more space for it. Surgery is generally a last resort but is often successful in reducing symptoms long-term.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adjustments like reducing salt intake, managing weight, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help reduce CTS symptoms. Avoiding caffeine and nicotine may also benefit some individuals, as these can contribute to inflammation.
Conclusion
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be frustrating, especially if symptoms continue to worsen despite your best efforts. By identifying the underlying causes and making necessary adjustments, you can take control of your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Remember to prioritize early intervention, ergonomic adjustments, and consistent self-care, and don’t hesitate to seek professional advice for persistent symptoms..