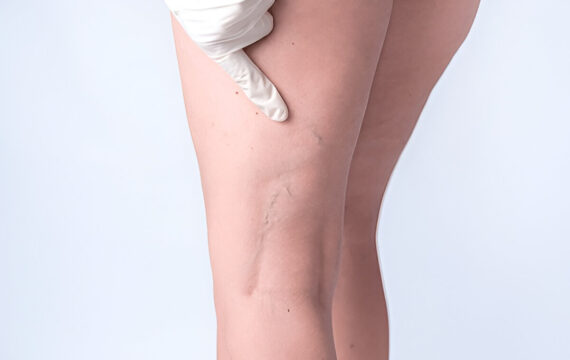
Vein ablation has become a popular procedure to treat chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins, both of which cause significant discomfort and cosmetic concerns for many individuals. This minimally invasive technique uses heat or chemicals to close off problematic veins, rerouting blood through healthier veins. Although vein ablation can bring substantial benefits, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons carefully.
What is Vein Ablation?
Vein ablation refers to methods that eliminate the function of malfunctioning veins by sealing them shut. The two main types are endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA), both of which use heat. An alternative, sclerotherapy, involves injecting a solution to irritate and close the vein. Each method has its unique mechanism, but the outcome is the same: treated veins close off, and blood flow is redirected.
Pros of Vein Ablation
- Effective Treatment for Varicose Veins and Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- Vein ablation offers high success rates, often around 90-95% for those undergoing RFA or EVLA. Patients experience significant improvement in symptoms, such as leg heaviness, swelling, pain, and even skin changes, which may enhance overall quality of life.
- Minimally Invasive and Quick Recovery
- Vein ablation is minimally invasive, requiring only small incisions or injections with local anesthesia. This allows for a faster recovery time than traditional vein stripping surgery. Most patients can resume regular activities within a day or two.
- Outpatient Procedure with Minimal Downtime
- The procedure is typically completed in an outpatient setting, taking about 30–60 minutes, which makes it a convenient option for many. Given its minimal downtime, patients experience little disruption to their schedules.
- Reduced Pain and Minimal Scarring
- Vein ablation causes minimal discomfort during and after the procedure, especially compared to vein stripping, which historically involved a more extensive surgical approach. Since ablation requires only small incisions, scarring is usually minimal or absent, which makes it cosmetically preferable.
- Low Risk of Complications
- Complications are rare, and when they occur, they are typically mild, such as bruising, swelling, or tenderness around the treated area. Serious complications, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or nerve damage, are infrequent with modern ablation techniques.
Cons of Vein Ablation
- Potential for Recurrence
- While vein ablation has high initial success rates, some patients may experience recurrence of symptoms or varicose veins in the same or nearby areas after several years. This may require follow-up treatments, which can lead to additional time and expense.
- Not Suitable for All Patients
- Certain medical conditions or anatomical features may make some patients ineligible for vein ablation. Patients with blood-clotting disorders, infections, or veins too small to accommodate the catheter may need alternative treatments.
- Possible Side Effects
- Though rare, vein ablation can lead to side effects such as bruising, skin discoloration, or numbness. Infrequently, heat-based methods may lead to burns, while sclerotherapy may cause temporary pigmentation along the treated vein.
- Expense and Insurance Considerations
- The cost of vein ablation varies widely, especially when considering follow-up treatments or additional sclerotherapy sessions for cosmetic purposes. While many insurance providers cover vein ablation if it’s deemed medically necessary, cosmetic procedures are generally not covered, and out-of-pocket costs can be substantial.
- Potential for Nerve Damage
- Ablation procedures carry a small risk of nerve damage due to the proximity of some veins to nerves, particularly in the leg. This may lead to persistent numbness or discomfort in some patients, although such cases are rare.
Is Vein Ablation Right for You?
For individuals with symptomatic varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency, vein ablation is a promising, minimally invasive solution with a high success rate. However, for those with only minor cosmetic concerns or particular health conditions, the cons may outweigh the benefits. Consulting a vascular specialist for a comprehensive evaluation is the best way to determine if vein ablation suits one’s unique situation.
Conclusion
Vein ablation has transformed the treatment landscape for varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency, offering an effective, minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgery. The pros—such as rapid relief, minimal recovery time, and cosmetic appeal—make it an appealing option. However, understanding potential cons, including recurrence, side effects, and financial considerations, is essential in making an informed decision. Consulting a healthcare professional can help you determine the best course of action for your vein health. ls.