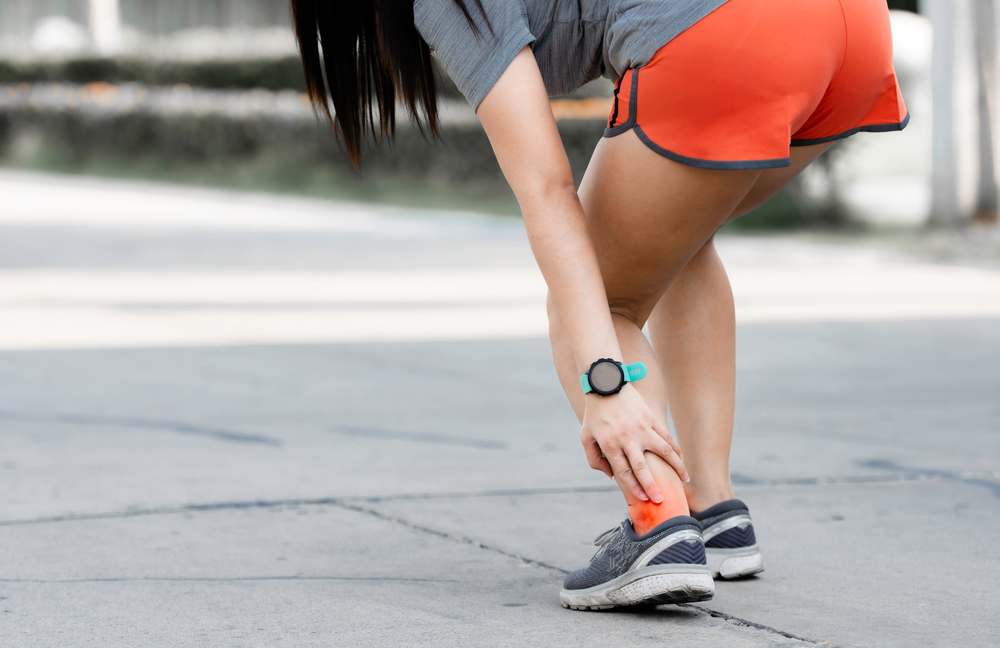
Achilles tendonitis is a common but often debilitating condition that can significantly impact your daily life and physical activity. As the largest tendon in your body, the Achilles tendon connects your calf muscles to your heel bone, playing a crucial role in walking, running, and jumping. When this tendon becomes inflamed or irritated, it leads to Achilles tendonitis, a condition marked by pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Understanding Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis typically occurs due to overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon. It is commonly seen in athletes, particularly runners, but can affect anyone, especially those who suddenly increase their activity level or engage in activities requiring intense physical exertion.
Causes of Achilles Tendonitis
Several factors can contribute to the development of Achilles tendonitis, including:
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the tendon from activities like running, jumping, or high-intensity sports can lead to inflammation.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: A rapid increase in the intensity or duration of physical activity can overload the tendon.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can strain the Achilles tendon.
- Tight Calf Muscles: Limited flexibility in the calf muscles can put extra stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Foot Structure: Flat feet or high arches can alter the biomechanics of the foot, increasing the risk of tendonitis.
- Age: As you age, the Achilles tendon becomes less flexible and more prone to injury.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis manifests through various symptoms, which may include:
- Pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, especially in the morning
- Swelling around the affected area
- Tenderness or discomfort when touching the tendon
- Limited range of motion in the ankle
- A creaking or crackling sensation when moving the tendon
Treatment Options
Effective management of Achilles tendonitis involves a combination of self-care measures, medical treatments, and physical therapy. Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or temporarily stopping activities that aggravate the tendon is crucial for recovery. Gradually reintroduce physical activity as the pain subsides.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression and Elevation: Using compression bandages and elevating the foot can minimize swelling and promote healing.
- Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to strengthen the calf muscles, improve flexibility, and correct any biomechanical issues.
- Orthotics and Footwear: Custom orthotic inserts and supportive footwear can help reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT): This non-invasive treatment uses shockwaves to stimulate healing in the tendon.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the damaged tendon.
Preventive Measures
Preventing Achilles tendonitis involves adopting healthy habits and making modifications to your routine. Here are some preventive measures:
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of your physical activities. Gradually build up your exercise routine.
- Proper Warm-Up: Always warm up before engaging in physical activity to prepare your muscles and tendons.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate regular stretching and strengthening exercises for your calf muscles and Achilles tendon into your routine.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Choose shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning. Replace worn-out shoes regularly.
- Cross-Training: Include a variety of exercises in your fitness regimen to avoid overloading the Achilles tendon with repetitive strain.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort and address them promptly to prevent further injury.
Conclusion
Achilles tendonitis can be a painful and frustrating condition, but with proper understanding, treatment, and preventive measures, you can overcome the agony and return to your active lifestyle. By taking proactive steps to manage and prevent Achilles tendonitis, you can protect your tendon health and enjoy a pain-free, active life. If you experience persistent pain or discomfort, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.