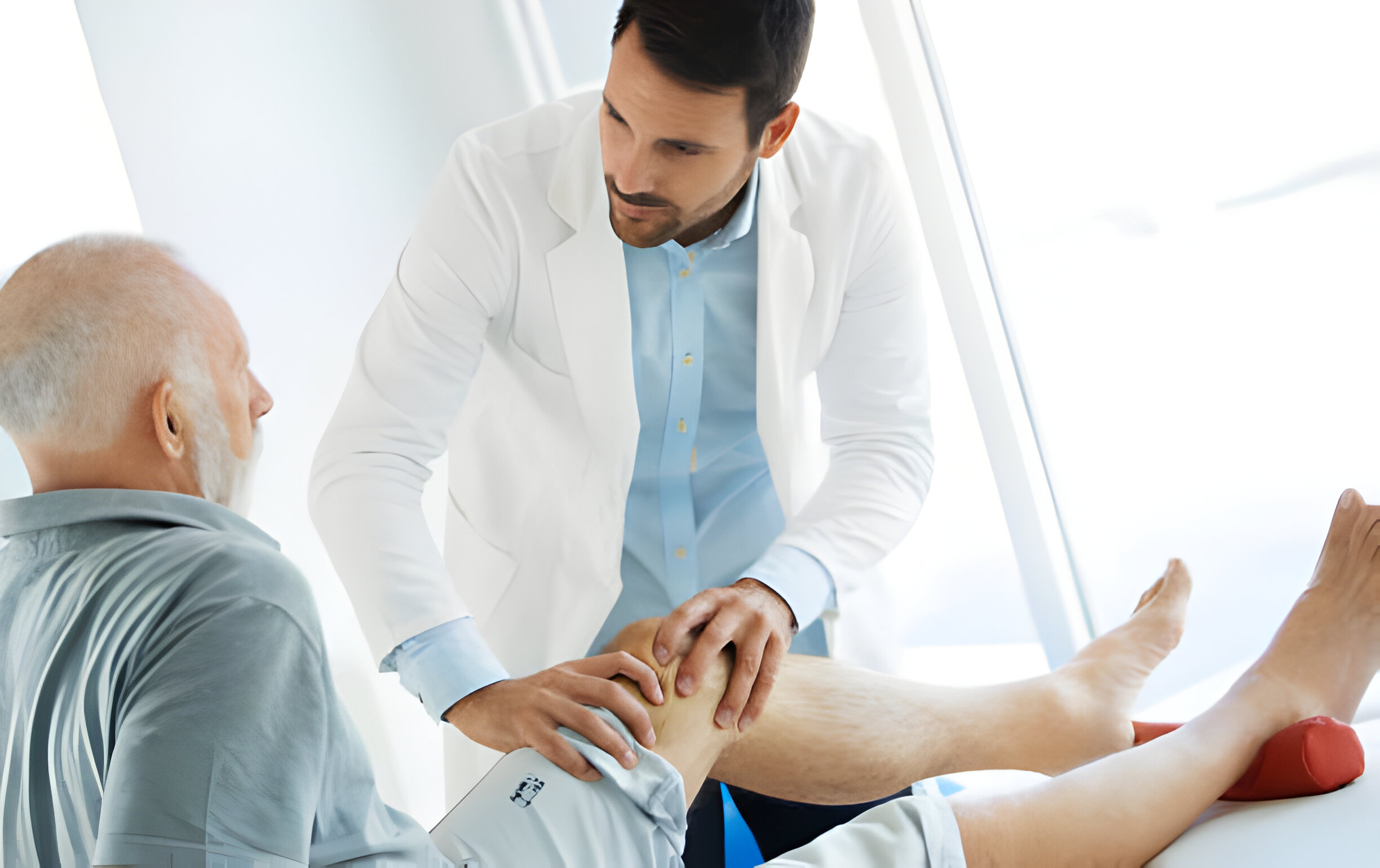
Knee pain can significantly impact one’s daily life, making even the simplest activities challenging. Among the various types of knee pain, side knee pain is particularly troublesome, often baffling patients and healthcare providers alike. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Common Causes of Side Knee Pain
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
The iliotibial band (IT band) is a thick band of tissue that runs along the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee. ITBS occurs when this band becomes tight or inflamed, causing pain on the outer side of the knee. This condition is common among runners and cyclists due to repetitive bending and extending of the knee.
Lateral Meniscus Tear
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia). A tear in the lateral meniscus, located on the outer side of the knee, can result from sudden twisting or trauma. This injury often leads to pain, swelling, and a limited range of motion.
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injury
The LCL is one of the ligaments that stabilize the knee joint, running along the outer side of the knee. Injuries to the LCL can occur due to direct blows to the inner side of the knee or excessive outward force. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and instability in the knee.
Bursitis
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between bones and soft tissues. Inflammation of the bursa on the outer side of the knee, known as bursitis, can cause pain and swelling. This condition often results from overuse, repetitive movements, or direct trauma to the knee.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can affect any part of the knee, including the outer side. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the bones wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults but can affect anyone with a history of knee injuries or excessive strain on the joints.
Diagnosing Side Knee Pain
Accurate diagnosis of side knee pain involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Healthcare providers may ask about the onset, duration, and nature of the pain, as well as any activities that exacerbate or alleviate it.
A physical examination can help identify areas of tenderness, swelling, and instability. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the internal structures of the knee and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for side knee pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
- Rest and Activity Modification Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and allowing time for healing is often the first step. Gradual return to activity, with modifications to avoid repetitive stress, can help prevent recurrence.
- Physical Therapy Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall knee stability. Therapists may also use techniques such as ultrasound, ice, or heat therapy to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Medications Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended for more severe inflammation.
- Bracing and Support Wearing a knee brace or support can provide stability and reduce stress on the affected area. This is particularly useful for ligament injuries or conditions like ITBS.
- Surgical Intervention In cases of severe injury or persistent pain that does not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be necessary. Procedures can range from minimally invasive arthroscopy to repair or remove damaged tissue, to more extensive surgeries such as ligament reconstruction or partial knee replacement.
Preventing Side Knee Pain
Preventing side knee pain involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adopting habits that protect your knees. Regular exercise, focusing on strength and flexibility, can keep the muscles and ligaments around the knee strong and resilient. Proper footwear, especially for athletes, can reduce stress on the knees. Additionally, avoiding sudden increases in activity intensity and incorporating rest periods into your routine can help prevent overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Side knee pain can stem from various conditions, each requiring a tailored approach for effective management. By understanding the potential causes and seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment, people can alleviate pain and restore knee function. If you are experiencing persistent side knee pain, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to identify the underlying issue and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.